What is an Overflow Valve Block and How Does It Work?
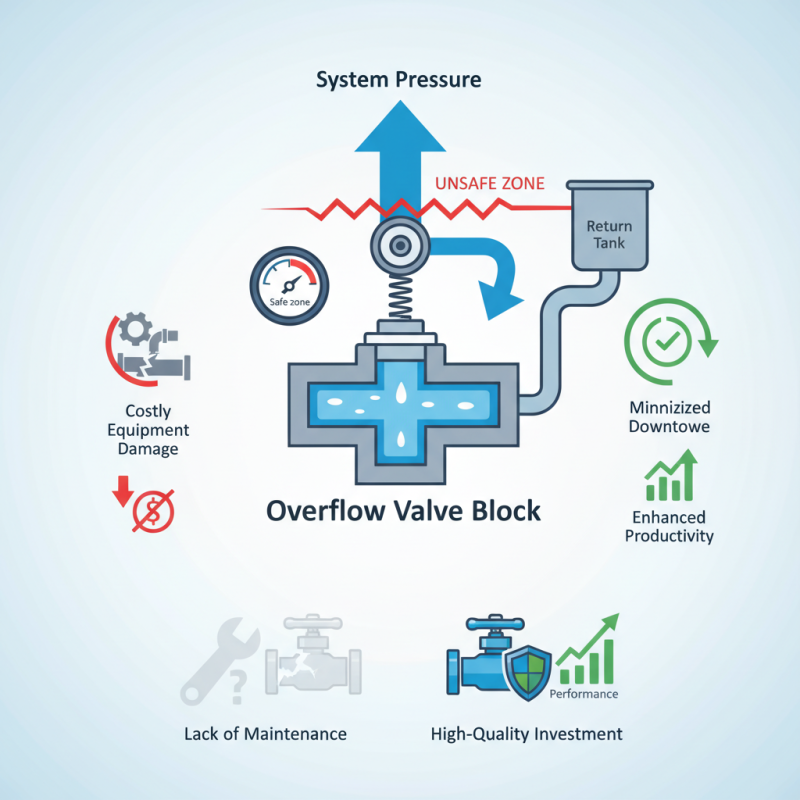
An Overflow Valve Block is crucial in fluid control systems. Its primary function is to prevent system pressure from exceeding safe levels. According to industry reports, failure to manage pressure can result in costly equipment damage, highlighting the importance of this component.
The mechanism behind an Overflow Valve Block is straightforward yet pivotal. It monitors and regulates fluid flow, ensuring that excess pressure is safely diverted. Studies indicate that effective use of overflow valves minimizes downtime. This can enhance productivity by up to 15%.
Despite its importance, some systems still lack efficient overflow solutions. Many operators overlook maintenance, leading to preventable failures. This raises questions about best practices in equipment management. Investing in high-quality Overflow Valve Blocks can significantly improve overall system performance.
What is an Overflow Valve Block and Its Primary Functions
An overflow valve block is a crucial component in hydraulic systems. It prevents excessive pressure build-up by diverting fluid when necessary. This mechanism is vital in ensuring system safety and reliability. According to industry reports, proper pressure regulation is essential for many applications, as it can reduce wear on components by up to 30%.
The primary function of an overflow valve block is to maintain consistent pressure levels. It activates when pressure thresholds are exceeded, releasing excess fluid back to the reservoir. This not only protects the system but also optimizes performance efficiency. Data from the Engineering and Manufacturing Association indicates that using a well-designed overflow valve can increase overall system efficiency by 15%.
However, not all overflow valve blocks perform equally. Variations in design and materials can lead to inconsistent pressure control. Some systems may experience delays in activation, leading to potential overflow situations. Regular maintenance and testing can help mitigate these risks, ensuring that the valve block functions effectively. Reportedly, nearly 20% of machinery failures are linked to inadequate pressure management, highlighting the importance of vigilant system care.
Components of an Overflow Valve Block and Their Significance
An overflow valve block is essential in many hydraulic systems. It regulates pressure and prevents excess fluid from causing damage. Key components include the valve itself, springs, and ports. Each part plays a vital role.
The valve is responsible for controlling fluid flow. It opens and closes based on the pressure levels detected. Springs provide necessary response and feedback. If they wear out, it can cause malfunction. Ports connect the valve to the hydraulic circuit. Proper seals here are crucial to avoid leaks.
Understanding these components helps in maintenance. Identify wear and tear proactively. An overlooked spring or damaged seal can lead to inefficiency. Regular checks are key to system longevity. Consistent evaluation of these parts ensures smooth operation. In complex systems, even minor issues can escalate. Proper oversight can prevent costly downtime.
How Overflow Valve Blocks Regulate Pressure in Hydraulic Systems
An overflow valve block is crucial in hydraulic systems. It helps maintain the right pressure levels. This functionality prevents system overload and potential damage. When pressure exceeds a set point, the valve opens. Fluid flows back to the reservoir, reducing excess pressure.
These overflow valve blocks regulate the pressure effectively. They prevent malfunctions due to high pressure. However, sometimes they fail or don't respond correctly. This can lead to dangerous situations. Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance. Operators should inspect these components regularly. A missed inspection can result in significant failures.
Hydraulic systems depend on precise pressure control. Proper function of overflow valve blocks enhances system reliability. Yet, failure to address wear may cause inefficiency. Understanding the role of these components is vital. Observing them can prevent costly downtime.
Pressure Regulation in Hydraulic Systems using Overflow Valve Blocks
Common Applications of Overflow Valve Blocks in Industrial Machinery
Overflow valve blocks play a crucial role in managing fluid systems. These devices help control excess fluid pressure and maintain system integrity. In many industrial applications, they prevent damage to machinery components. That’s essential for maintaining efficiency.
One common application is in hydraulic systems. Here, overflow valve blocks protect pumps from overpressure situations. They redirect excess fluid back to the tank. This helps avoid costly repairs and equipment failure. In manufacturing, these devices ensure smooth operation. They can enhance the productivity of assembly lines.
Chemical processing is another area where overflow valve blocks are used. They maintain stable pressure levels during mixing processes. However, it’s important to regularly inspect these valves. Neglect can lead to leaks or pressure spikes. This could compromise safety. An understanding of these applications is essential. It allows industries to implement preventive measures effectively.
Performance Standards and Specifications for Overflow Valve Blocks
Overflow valve blocks are essential for hydraulic systems. They regulate fluid pressure and protect components from damage. Understanding performance standards is crucial for effective usage.
Performance specifications vary widely. Common metrics include pressure ratings, flow capacity, and response time. Manufacturers often outline criteria in their documentation. However, there can be inconsistencies.
One might find that a block labeled for high pressure fails at unexpected levels. This inconsistency can lead to operational inefficiencies.
Regular testing is necessary to ensure standards are met. Yet, how often do users actually perform these tests? Very few operators schedule regular maintenance checks. This oversight can result in catastrophic failures. Users must be aware of the risks involved. Reliability comes from understanding the specifications and monitoring performance diligently.

